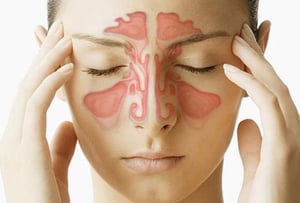
 Also called sinusitis, a sinus infection, is a common and painful condition that causes stuffy, painful pressure in the nasal cavity.
Also called sinusitis, a sinus infection, is a common and painful condition that causes stuffy, painful pressure in the nasal cavity.
Sinusitis affects around 31 million people in America each year. Most cases of sinusitis are due to a virus and will go away on their own. Viral sinusitis is contagious, so take steps to avoid passing it on to other people.
Bacteria, and in rare cases a fungus, might also be responsible for causing sinusitis.
It can be challenging to tell sinusitis apart from a cold or allergy, so knowing the symptoms of a sinus infection can help with finding the best treatment.
Eleven symptoms of a sinus infection
1. Sinus pain and pressure
Fluid trapped in the sinuses can fill the sinus cavities, causing intense pain and pressure. The sinuses may be sensitive to the touch. A person may have an urge to sneeze but be unable to do so.
The pain can be in the cheeks, around the eyes and nose, or in the forehead because these areas are where the sinuses are. Bending over may make the pain worse.
2. A headache
The pressure and pain of sinusitis can cause headaches in the front of the head. Some people find that the pain radiates elsewhere, causing more widespread problems or even neck pain.
3. Postnasal drip
Postnasal drip is mucus that drips from the nose down to the back of the throat. It can cause feelings of hoarseness and congestion, or a sense of pressure in the throat or mouth.
4. Congestion
A person with a sinus infection might have a viral infection or, less commonly, a bacterial or fungal infection in their sinuses. This usually happens where there is fluid trapped in the sinuses in which viruses, bacteria, or fungus can grow. Because of the fluid buildup and inflammation, a person is likely to feel congested.
5. Coughing
A sinus infection can cause mucus and fluid to back up in the throat, which may make the throat itch or feel full. Some people repeatedly cough to try to clear the throat, but others experience uncontrollable coughing.
6. Fever
A fever is a sign that the body is fighting off an infection. Some people develop a fever with a sinus infection. Other symptoms associated with fever include chills, exhaustion, and muscle aches.
7. Brightly colored mucus
Viruses, bacteria, or fungus in the mucus can change its color. People with sinus infections often notice that they cough up green or yellow phlegm, or that the mucus they blow out of their nose is a bright color.
Sinusitis causes a lot of mucus production, and a person may find they are unable to clear the sinuses no matter how often they blow their nose.
8. Fatigue
Fighting a sinus infection demands energy from the body, so it is common to feel fatigued. Some people feel exhausted because they cannot breathe easily or are in pain.
9. Bad breath
The mucus associated with a sinus infection may have a bad odor, which can cause smelly breath or a bad taste in the mouth.
10. Tooth pain
Intense sinus pressure can cause pain in the gums, which can lead to toothaches, gum pain, or general pain in the mouth.
11. Chronic sinus pain
Some sinus infections can become chronic. Anyone who experiences sinus pain and pressure that lasts several weeks and that is unrelated to an allergy or infection might have chronic sinusitis.
Is It a Sinus Infection or Cold?
It can be difficult to tell the difference between a sinus infection and a cold as the symptoms can be very similar. Sinus infections often develop after a cold.
Sinusitis tends to last longer than a cold. Cold symptoms tend to get steadily worse, peaking at 3–5 days, then gradually get better. Sinus infections may last 10 days or more.
Some symptoms are more likely to be caused by sinusitis than a cold, including:
- swelling of the tissue in the nose
- bad breath
- green discharge from the nose
- swollen or tender face
Unlike a cold, sinusitis can become chronic, which means it lasts longer than 3 months. Chronic sinusitis causes swelling and irritation in the sinuses and usually develops after a person has had acute sinusitis. Sometimes the symptoms go away and then come back again. Ongoing sinus symptoms —even if they get better and then come back — may indicate chronic sinusitis.
Treating a Sinus Infection
Sinus infections often go away on their own without medical treatment. There are, however, some things a person can do at home to relieve the bothersome symptoms.
To treat sinusitis symptoms with home remedies, try:
- Applying a warm compress to the sinuses, which eases pain and pressure by loosening up the fluid in the sinuses.
- Using a nasal wash or sinus rinse, such as a saline spray or neti pot, which are available from drug stores and online.
- Taking antihistamine tablets to reduce inflammation in the sinuses; there is a variety of antihistamines available in supermarkets and online.
- Using a nasal decongestant spray to help clear the sinuses and relieve pressure. These sprays are also available to buy from drug stores or online.
Avoid using decongestants on a long-term basis without talking to a doctor first because they can make congestion worse if used for too long.
When to see a doctor
A person may wish to talk to their doctor if:
- symptoms last longer than 7 to 10 days
- a child has a fever for more than a day or two
- the pain is very intense
- a person with a suspected sinus infection has a weakened immune system due to a medical condition, drugs that suppress the immune system, or organ failure

